RACI Matrix for better Project Management
Overview
RACI matrix: The huge benefits of task specific roles
In a common project plans each task is assigned to one or more team members supposed to take care of it. The RACI matrix extends the number of relationships people can have with a task beyond that making somebody responsible for it.
This makes sense because the caretakers are oftentimes not the only ones involved in these tasks. For example, others might want to know when a task is finished, or information from other project participants is needed to complete a task.

The RACI method provides four task specific roles through which project stakeholders can relate to a task. Usually people are assigned roles to a project on the whole, for example somebody is manager for system integration or Scrum master. RACI gives us much more flexibility as its roles can be different for different people on different tasks.
The RACI matrix does not replace other management methods such as work breakdown structures, Gantt charts or network plans, but supplements them. The RACI matrix is also called the “Responsibility Assignment Matrix” (RAM).
With the RACI method, the responsibilities in a project or company can be presented in a clear, differentiated and concrete way. As a result, many people found that their project work became more efficient. In general, there were fewer misunderstandings as each persons role was clear and everybody knew their assignments. In project meetings, the number of lengthy and fruitless discussions decreased. Decisions were made faster and the workload was distributed more fairly.
Better management with the RACI chart
The RACI chart places all tasks in rows and the project members in columns. The intersecting field of task and project member contains the roles that person has with this task.
There are four types of relationships or roles in the RACI system:
- the Responsible – she takes care of the task, looking for a way to complete it on time and on budget
- the Accountable (Manager) – she makes decisions and takes action for the tasks.
- the Consulted – he is involved and informed about decisions and tasks
- Informed – He will be informed about decisions and actions during the project
In the intersecting fields you enter an R, A, C or I, or you leave it empty. There should only be one R for each task, ie there should not be more than one R per row in the matrix.
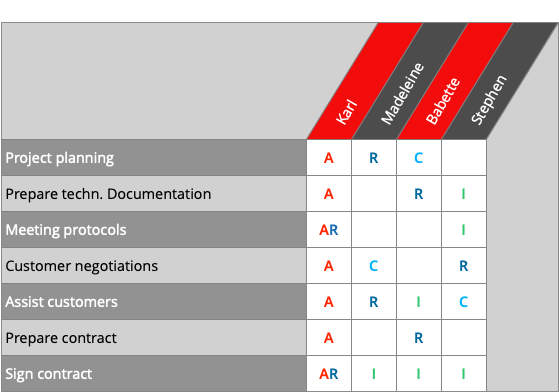
RACI example
To explain the RACI principle, we will use the matrix above. Karl is the decision maker (Accountable) for questions about the process “Project planning”. Madeleine is the responsible person for the execution of the project planning. And Babette can be called in as a consultant because she knows about the dependencies between this project and her own decision, and can alert Madeleine to potential conflicts. Stephen basically gets copies of the minutes of meeting (Informed) because he needs this information to manage his own work.
How does RACI help you?
Properly applied, the RACI method offers you a whole range of advantages:
- Transparency: The RACI matrix clearly shows who is responsible for what. This avoids unnecessary discussions and eliminates misunderstandings.
- Fair workload distribution: The chart makes it visible when individual employees have been assigned too many or too few tasks.
- No bottlenecks: It becomes clear when employees appear as advisers in too many places and thus possibly slow down project progress.
- Targeted communication: If an employee is registered as informed in almost every field, one must question whether this is really necessary. The RACI Matrix helps to build an efficient communication scheme in projects. Information thus systematically reaches where it is useful. Unnecessary communication according to the watering can principle is avoided.
Setting up the schema
Here is in brief how you set up an appropriate schema for your project:
- Create a list of project tasks
- Identify the project participants
- For each task or process, identify an editor and a manager
- Make sure that there is only one editor per task
- Speak to all editors and managers and make sure everyone understands their role and role.
- Add consulted and informed if necessary.
Tips on the RACI matrix
- The RACI matrix should not be misused as a control tool. The RACI Matrix does not help to fix a disfunctional team. The team spirit has to be right and there has to be confidence.
- The tasks in the matrix must be clearly and comprehensibly formulated.
- The scope of a task must be clear. For example, specify in a project handbook who is responsible for creating and maintaining the RACI Matrix itself.
- Determine whether an adviser can and must become active on his own or only on request.
- Make it clear that it is not the manager who is responsible for a task, but the project manager. Of course it is also possible that both roles are represented by the same person.
- Make sure that each line has exactly one Responsible (R). It is rarely good if several people are responsible. If in doubt, divide a task into subtasks.
- Avoid bottlenecks with too many C’s in a row.
- Make sure the RACI matrix is integrated with regular project planning. It does not help much if you run the RACI matrix in an Excel spreadsheet and do the project planning and tracking work in another tool.
RACI and Agile
There are scrum experts who think that RACI does not fit Scrum without any customization. Although there are many variations of RACI, some practitioners feel the urge to have new Scrum-specific roles (like “F = Facilitator / Coach”), new Scrum-specific activities, and responsibilities (such as “ensuring the consistency of Scrum practices across teams or elimination of obstacles”), or to include new positions and roles (such as “Scrum Team”) in the matrix.
In the simplest case, according to the Scrum Handbook the Product Owner is the one and only person responsible for managing the Product Backlog. Even if the Product Owner assigns work to the development team, he remains accountable. According to Scrum, stakeholders are also accountable and must be involved in the overall process. They should therefore be treated as managers in the RACI Matrix. It is debatable how to integrate consulted and informed into the Scrum scheme.
RACI matrix variants
There are a number of variants of the RACI project management chart to clarify responsibilities and responsibilities. A relatively extensive list can be found on Wikipedia.
- DRASCI: Here are the roles “Driver” and “Support” added. The “Driver” supports the engineer in the management, while the “Support” assists him in the execution level.
- RASCI: The standard RACI matrix with consulted roles plus the one taking on responsibility is supplemented by “support”, ie the persons who support the “responsible” person in carrying out a task. RACI-VS: There are two further areas: If a role is assigned a “Verify”, it should check whether the defined product properties have been implemented as desired. “Signatory” means that a person approves the “Verify” result. In comparison to the standard RACI, further test steps are built in here.
- CAIRO: Almost the standard RACI, only supplemented by “Omitted”. If this value is assigned, participants are deliberately excluded from a task. Otherwise we have the standard accountable role, consulted role, a person that assumes responsibility and does the main work, and the role of the informed.
To learn more about RACI chart as it is implemented in the project management software and task management software Allegra have a look at our RACI white paper.
More keywords: work, consulted, one, responsibility, roles, team, work, chart




